Fullstack Data Flow
Fullstack Data Flow
One of the primary features of Remix is the way it automatically keeps your UI in sync with persistent server state. It happens in three steps:
- Route loaders provide data to the UI
- Forms post data to route actions that update persistent state
- Loader data on the page is automatically revalidated
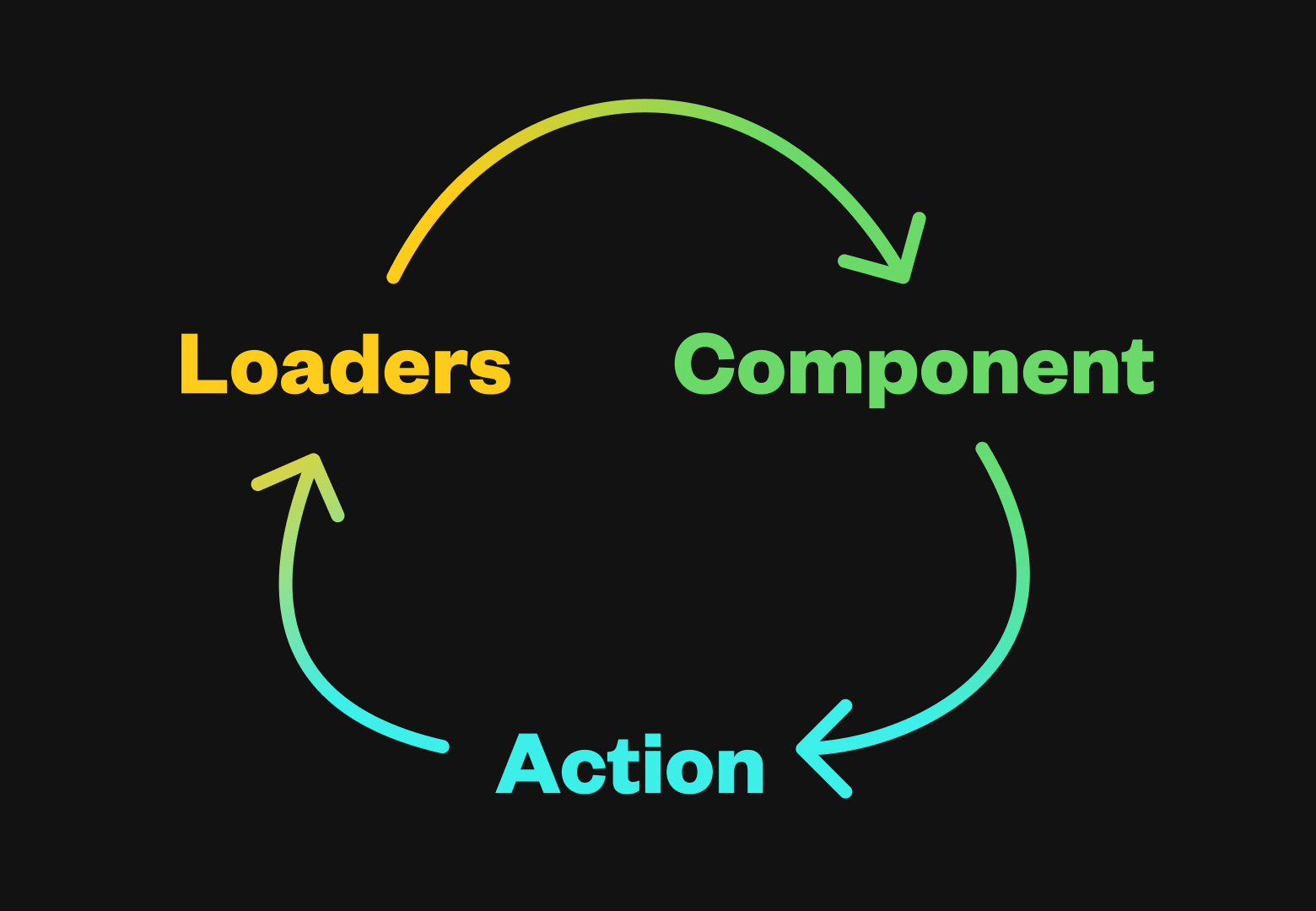
Route Module Exports
Let's consider a user account edit route. The route module has three exports that we'll fill in and talk about:
export async function loader() {
// provides data to the component
}
export default function Component() {
// renders the UI
}
export async function action() {
// updates persistent data
}
Route Loader
Route files can export a loader function that provides data to the route component. When the user navigates to a matching route, the data is first loaded and then the page is rendered.
export async function loader({ request }) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return {
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
};
}
export default function Component() {
// ...
}
export async function action() {
// ...
}
Route Component
The default export of the route file is the component that renders. It reads the loader data with useLoaderData:
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react";
export function loader({ request }) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return {
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
};
}
export default function Component() {
const user = useLoaderData();
return (
<Form action="/account">
<h1>Settings for {user.displayName}</h1>
<input
name="displayName"
defaultValue={user.displayName}
/>
<input name="email" defaultValue={user.email} />
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</Form>
);
}
export function action({ request }) {
// ...
}
Route Action
Finally, the action on the route matching the form's action attribute is called when the form is submitted. In this example it's the same route. The values in the form fields will be available on the standard request.formData() API. Note the name attribute on the inputs is coupled to the formData.get(fieldName) getter.
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react";
export function loader({ request }) {
const user = await getUser(request);
return {
displayName: user.displayName,
email: user.email,
};
}
export default function Component() {
const user = useLoaderData();
return (
<Form action="/account">
<h1>Settings for {user.displayName}</h1>
<input
name="displayName"
defaultValue={user.displayName}
/>
<input name="email" defaultValue={user.email} />
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</Form>
);
}
export function action({ request }) {
const user = await getUser(request);
await updateUser(user.id, {
email: formData.get("email"),
displayName: formData.get("displayName"),
});
return { ok: true };
}
Submission and Revalidation
When the user submits the form:
- Remix sends the form data to the route action.
- After the action completes, loaders are revalidated to get the new server state.
useLoaderDatareturns the updated values from the server.
In this way, the UI is kept in sync with server state without writing any code for that synchronization.
There are various ways to submit a form besides an HTML form element (like in response to drag and drop, or an onChange event). There is also a lot more to talk about around form validation, error handling, pending states, etc. We'll get to all of that later, but this is the gist of data flow in Remix.